
menu

Posted in Uncategorized | December 6, 2022

Does your child constantly complain about ear pain? Does it seem like they always have an ear infection?
Chronic ear infections can lead to hearing loss and other long-term health complications without timely treatment. For this reason, seeing an ENT specialist is very important if you suspect you or your child has a chronic ear infection.
If chronic ear infections are to blame, you can begin treatment and determine how to stop further ones from occurring, helping everyone in your family maintain good hearing.
Keep reading to learn more about chronic ear infections and possible complications to watch out for.
A chronic ear infection can be due to repeated ear infections. It may also happen when you have an acute ear infection that leaves a hole in your eardrum, which doesn’t heal.
An acute ear infection occurs when the Eustachian tube becomes blocked. The Eustachian tube drains fluid from the middle ear to the back of the throat.
When it becomes blocked, it leads to a buildup of fluid. The fluid can become infected, causing pain and other symptoms.
Ear infections can affect anyone. However, they’re most common in children.
That’s because children’s Eustachian tubes are more horizontal, narrower, and shorter than in adults. The tubes make it more challenging for fluid to drain from the ear, increasing the likelihood of ear infections.
Children’s immune systems are also underdeveloped, leaving them less equipped to fight off infections, including ear infections.
The symptoms of a chronic ear infection are usually less intense than an acute infection. Also, they may be constant or can come and go.
Some of the signs of chronic ear infections are:

There are different causes of chronic ear infections. They include:
There are different kinds of ear infections, such as:
An inner ear infection is also known as labyrinthitis. These infections occur when your inner ear becomes irritated or swollen due to a cold, allergies, the flu, or meningitis.
If you have an inner ear infection, it can make you feel like your surroundings are moving when they aren’t. Experiencing this is a condition called vertigo.
Other symptoms of inner ear infections are:
The first line of treatment for inner ear infections is antibiotics.
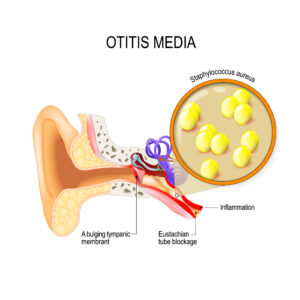
The middle ear is found between the oval window and the eardrum. It’s connected to your throat through the Eustachian tube.
A middle ear infection, also called otitis media, happens when germs from the throat and nose get trapped because of a blockage in the Eustachian tube. The infection can also occur due to chronic sinusitis or a viral infection in your sinus or nose.
Symptoms of a middle ear infection include:
Your ENT specialist may prescribe antibiotics or eardrops depending on the severity of the ear infection.
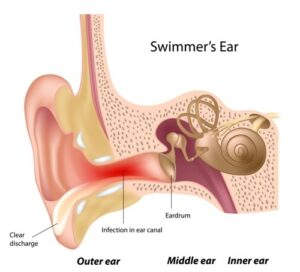
An outer ear infection is also called swimmer’s ear. You can develop an outer ear infection due to bacteria or fungi.
Bacteria may grow in the water trapped in your ear canal after bathing or swimming. This bacteria can cause an infection if you have a sore or scratch on your ear.
Symptoms of an outer ear infection include:
Usually, antibiotics are used to treat swimmer’s ear or an outer ear infection. But your ENT specialist will prescribe antifungal drops if you have an outer ear infection caused by a fungus.
Chronic ear infections can result in the following complications if they are not treated:
You can get cholesteatoma, also called a middle ear cyst, due to a chronic ear infection. The cyst comprises abnormal skin cells and other debris.
Cholesteatoma occurs when the vacuum pressure caused by an ear infection stretches your eardrum. Without timely treatment, the cholesteatoma can destroy delicate structures inside your ear that are vital for balance and hearing. You may experience hearing loss as a complication of cholesteatoma, meningitis, or the cyst spreading into the brain.
Mastoiditis is an infection of the mastoid bone behind your ear that aids with fluid drainage. Mastoiditis may start mild but worsens with repeated ear infections.
Some of the symptoms of mastoiditis are:

Swelling of the mastoid is a medical emergency. Your ENT specialist may drain your ear, deliver antibiotics intravenously, or perform surgery to remove any infected bone tissue.
If the infection continues to spread, it can lead to serious complications like:
Hearing loss from a chronic ear infection is often temporary. But if there’s damage to your eardrum or other structures in your middle ear, you may suffer permanent hearing loss.

If you or your child have recurring ear infections, it’s crucial to seek help from the experienced ENTs at Specialty Care ENT. Our team of specialists treats chronic ear infections in adults and children and can ensure you and your child find relief.
Do you or other members of your family suffer from frequent ear infections? Schedule an appointment today at Specialty Care ENT at one of our convenient locations in Barrington, Hoffman Estates, or Elgin, IL, for effective and safe treatment and to make recurring ear infections a thing of the past.